
Digital Rights Management (DRM) for PDF, Video & Web Pages
The internet has revolutionized how we create, share, and consume digital content. Books are now eBooks, classrooms have transformed into online learning platforms, movies are streamed globally, and business documents are exchanged in seconds. While this evolution has created incredible opportunities, it has also introduced a serious challenge — unauthorized copying, piracy, and redistribution of digital assets.
For authors, publishers, educators, film makers, and businesses, protecting intellectual property has become just as important as creating it. A single PDF can be duplicated infinitely, a premium training video can be screen-recorded and sold illegally, and confidential enterprise documents can be leaked without the owner ever knowing.
This is where Digital Rights Management (DRM) comes in. More than just copyright, DRM combines encryption, licensing, access control, and usage restrictions to ensure that only authorized users can access and use digital content. From eBooks to enterprise contracts, DRM acts as the gatekeeper, helping creators and organizations retain control, protect revenue, and maintain trust.
What is Digital Rights Management?
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a set of technologies, methods, and policies designed to control access, usage, and distribution of digital content. Unlike copyright, which relies on legal enforcement after infringement, DRM places technical barriers that prevent unauthorized copying or misuse before it happens.
In simple terms, DRM ensures that:
- Only the right people can open your content.
- Content can only be used in ways you approve (e.g., view-only, no print, no copy-paste).
- Access can be revoked at any time, even after files are downloaded.
DRM vs Copyright
- Copyright law gives creators ownership and the right to sue if their work is stolen
- DRM technology actively prevents unauthorized access or duplication from happening in the first place.
DRM vs Copy Protection
While often used together, DRM and copy protection differ slightly:
- Copy protection prevents duplication (e.g., blocking PrintScreen or downloads).
- DRM goes further by managing who can access, for how long, and under what conditions.
Real-Life Examples of DRM
- Apple iTunes: restricts music to licensed devices
- Netflix & Disney+: use DRM to stop movies being downloaded illegally.
- Amazon Kindle: eBooks tied to user accounts, preventing mass sharing.
- Microsoft & Adobe software: licensing systems prevent multiple unauthorized installations.
DRM is not just for big tech companies. Today, even small businesses, educators, and individual creators rely on DRM to safeguard their work.
Why Digital Rights Management Matters
1. Economic Impact
Digital piracy costs the global economy over $29 billion annually in lost revenue (U.S. Chamber of Commerce). For creators, every unauthorized download is a lost sale. For businesses, data leaks can cost millions in compliance fines and reputational damage.
2. Security & Compliance
Enterprises handle sensitive information like contracts, financial data, and customer records. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO standards require strict protection of digital information. DRM provides that control.
3. Preserving Creative Integrity
For artists and educators, DRM ensures that their work is not only protected financially but also used in the right context. An art piece shouldn’t end up in a misleading advertisement; a training video shouldn’t be resold illegally.
4. Trust & Reputation
Clients, students, and partners trust you with their data and intellectual property. DRM demonstrates professionalism and safeguards that trust.
Without DRM, your content is essentially open-source — free to copy, free to steal, free to exploit.
How Does DRM Work?
Although DRM systems vary, most follow a layered approach:
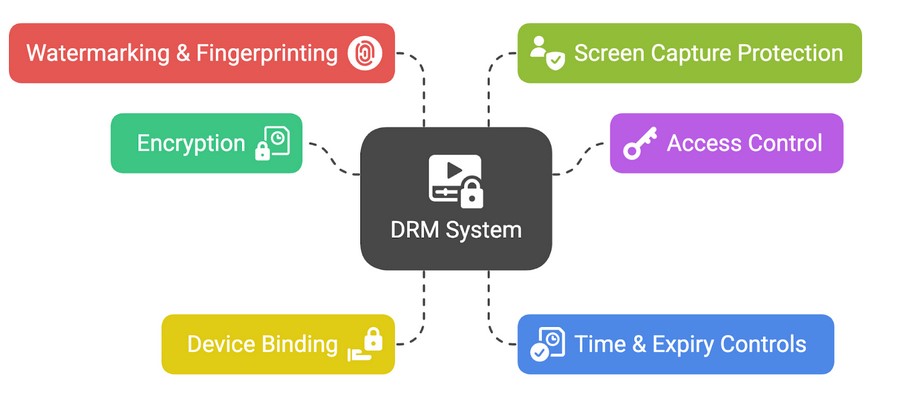
- Encryption
Content is encrypted so only authorized software or devices can open it. Without the correct license, files remain unreadable. - Access Control
Permissions define what users can do: view-only, print, copy, share, or download. - Device Binding
Files are locked to specific devices. For example, a PDF license might only open on a user’s laptop but not on a friend’s PC. - Time & Expiry Controls
Access can be time-limited — useful for subscriptions, training programs, or trials. Access can also be revoked remotely. - Watermarking & Fingerprinting
Dynamic watermarks embed user information (like name or email) to discourage leaks. - Screen Capture Protection
Prevents screenshots, screen recordings, and use of capture software.
Example Workflow: A publisher encrypts an eBook → uploads it to a server → grants access only to paying customers → customers download and open using a DRM-enabled reader → attempts to print, copy, or screenshot are blocked
This balance of encryption + control ensures creators retain full authority over their content.
Types of DRM Solutions
DRM for Documents & eBooks
- Protect PDFs, Word docs, and eBooks.
- Block copy-paste, printing, and sharing.
- Used by publishers, training providers, and researchers.
- Example: CopySafe PDF Protection.
DRM for Videos & Streaming
- Secure video players prevent screen recording.
- Stream encryption ensures only licensed users can watch.
- Used by eLearning, film studios, and OTT platforms.
- Example: CopySafe Video Protection.
DRM for Software & Apps
- License key validation.
- Prevents unauthorized installations and piracy.
- Common in enterprise SaaS and creative software.
DRM for Web Content
- Website encryption and protected browsers.
- Prevents saving, copying, or developer tool exploitation.
- Example: ASPS (ArtistScope Site Protection System).
DRM for Different Industries
- Publishing: eBooks, whitepapers, research documents.
- Education: eLearning platforms, online courses, exam materials.
- Corporate/Government: confidential files, contracts, reports.
- Media & Entertainment: movies, music, subscription-based streaming.
ArtistScope integrates DRM into WordPress, Moodle, Joomla, Drupal, and other popular platforms, making protection simple for every industry.
Common Myths & Criticisms of DRM
❌ "DRM frustrates users."
Modern DRM (like ArtistScope) is designed to be seamless while maintaining security.
❌ "Hackers always break DRM."
No system is 100% hack-proof, but system-level DRM is extremely difficult to bypass and acts as a strong deterrent.
❌ "Free tools are enough."
Free DRM tools are often easily cracked. Professional-grade DRM ensures robust, lasting protection.
Critics, including groups like the EFF, argue DRM limits freedom. But for businesses, the choice is simple: protect content or risk losing it entirely.
ArtistScope DRM – A Stronger Alternative
Since 1997, ArtistScope has pioneered DRM technologies that remain unbreakable and reliable. Unlike competitors, ArtistScope develops original solutions — not repackaged or token-based systems that hackers can easily bypass.
Exclusive Features of ArtistScope DRM
- Call-to-Home Validation: Real-time device & user verification.
- Device Locking: Files tied to hardware IDs for ultimate security.
- Content Revocation: Revoke access instantly, even post-download.
- Multi-Format Protection: Secure PDFs, videos, web content, and more.
- No Weak Links: Unlike competitors, ArtistScope solutions block all common exploits.
ArtistScope DRM Products
- CopySafe PDF Protection – capture-safe PDF DRM.
- CopySafe Video Protection – secure video DRM with screen capture blocking.
- ASPS Web Protection – site-wide DRM for web pages.
- SafeGuard Cloud Paywall – AI bot protection with DRM options.
- SafeGuard DRM & Media – plugins for WordPress and Moodle.
- SafeGuard Webmail – secure, DRM-protected email.
Comparison Example
| Feature | ArtistScope DRM | Generic DRM |
| Screen Capture Blocking | ✅ Yes | ❌ Limited |
| Device Binding | ✅ Strong | ⚠️ Weak |
| Revocation | ✅ Instant | ⚠️ Sometimes |
| Multi-Format Support | ✅ PDF, Video, Web | ❌ Limited |
The Future of DRM
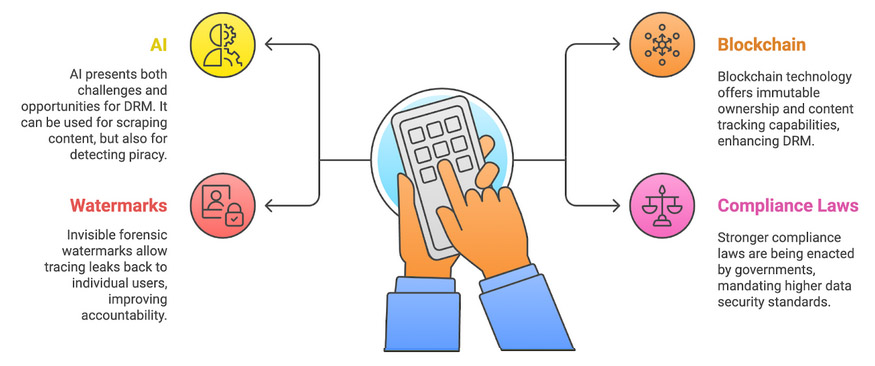
The DRM landscape is evolving:
- AI: Both a threat (scraping) and solution (piracy detection).
- Blockchain: Immutable ownership & content tracking.
- Invisible Forensic Watermarks: Trace leaks to individual users.
- Stronger Compliance Laws: Governments demanding higher data security.
The future is clear — strong DRM is no longer optional but essential.
FAQs About Digital Rights Management
Q1: What does DRM mean?
Digital Rights Management is a system that controls access and use of digital content to prevent piracy and unauthorized sharing.
Q2: How does DRM prevent piracy?
It uses encryption, device binding, watermarks, and capture-blocking to secure content.
Q3: Can DRM protect PDFs, videos, and software?
Yes, DRM is versatile and protects all major digital formats.
Q4: Is DRM only for large enterprises?
No. Creators, educators, and small businesses also benefit from DRM
Q5: Can access be revoked after sharing content?
Yes. With ArtistScope DRM, publishers can revoke access instantly.
Q6: What are real-world examples of DRM?
Netflix, Kindle, iTunes, and ArtistScope CopySafe solutions.
Q7: Is DRM legal?
Yes. DRM is supported under laws like DMCA and WIPO Copyright Treaty.
Conclusion & Call to Action
In a digital-first world, DRM is not optional — it’s a necessity. From protecting eBooks and videos to safeguarding confidential corporate files, DRM ensures that only the right people have the right access at the right time.
With over two decades of innovation, ArtistScope provides the most secure DRM solutions on the market, trusted worldwide by publishers, educators, governments, and enterprises.
🔒 Ready to protect your digital assets? Get Started with ArtistScope DRM